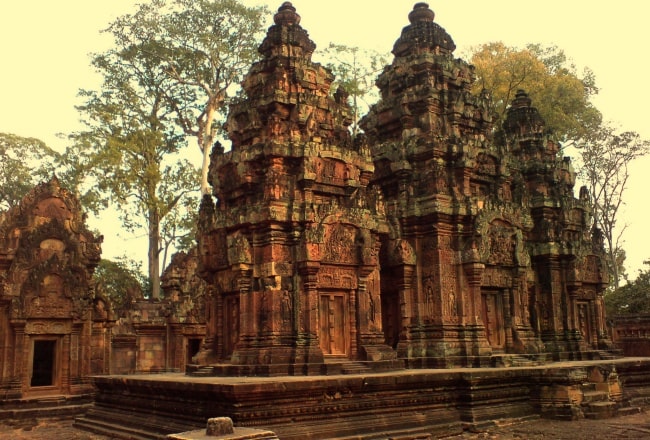
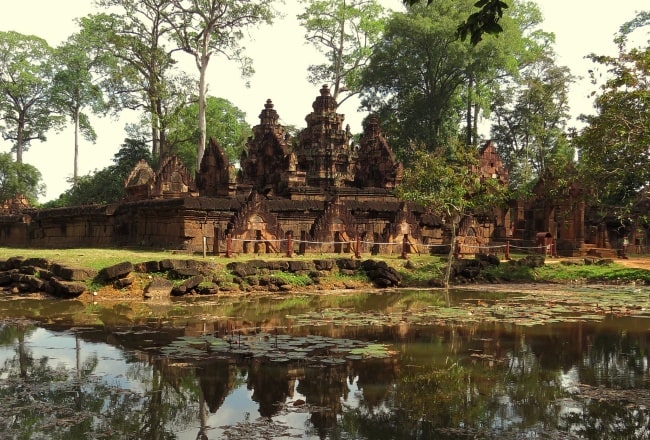
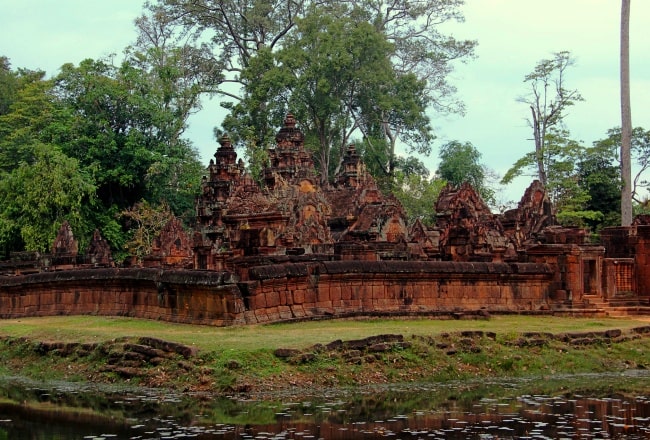
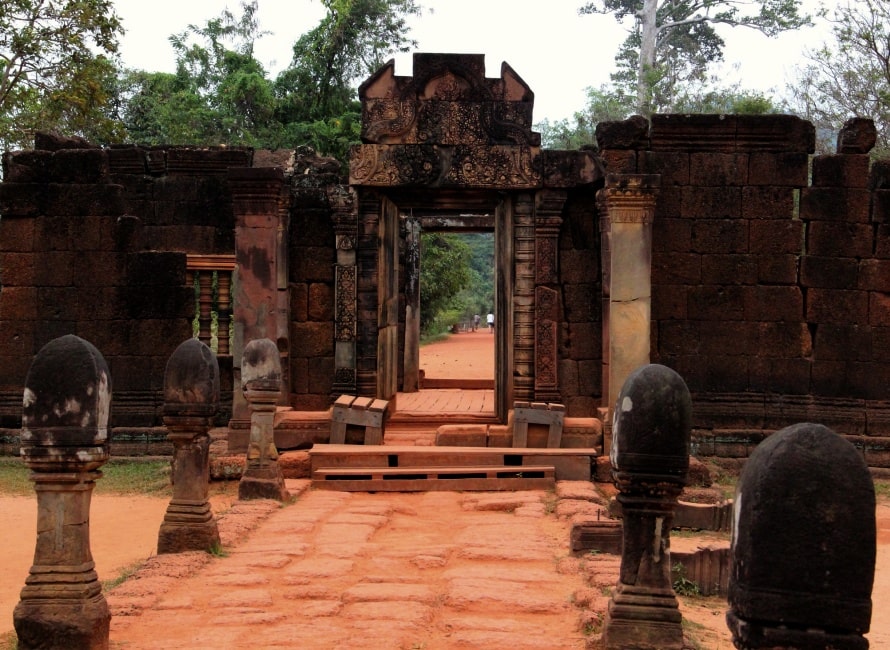
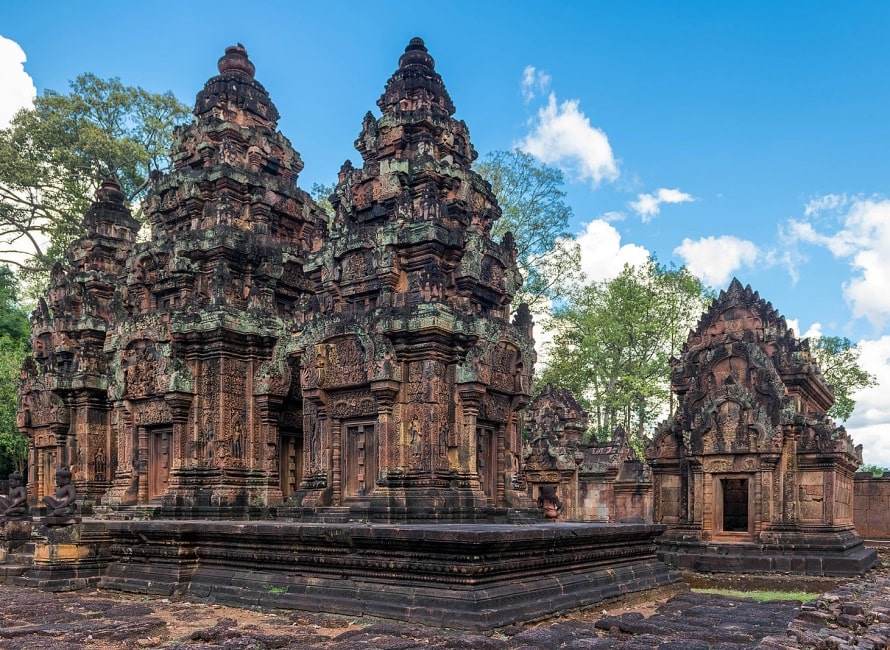
The site consists of three concentric rectangular enclosures constructed on an east–west axis. A causeway situated on the axis leads from an outer gopura, or gate, to the third or outermost of the three enclosures. The inner enclosure contains the sanctuary, consisting of an entrance chamber and three towers, as well as two buildings conventionally referred to as libraries.
The outer gopura
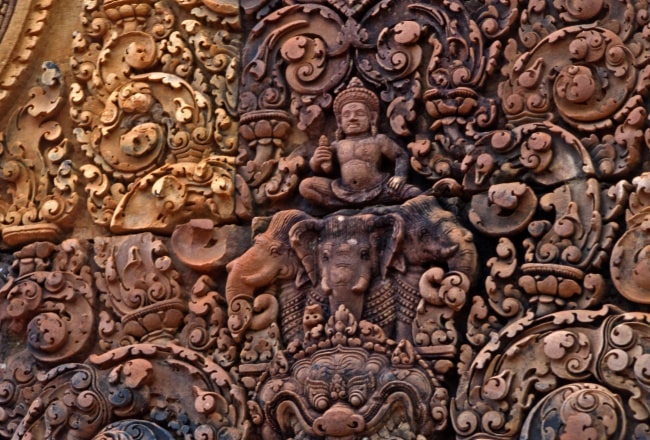
The gopura is all that remains of the outer wall surrounding the town of Isvapura. The wall is believed to have measured approximately 500 m square, and may have been constructed of wood. The gopura's eastern pediment shows Indra, who was associated with that direction, mounted on his three-headed elephant Airavata. The 67 m causeway with the remains of corridors on either side connects the gopura with the third enclosure. North and south of this causeway are galleries with a north–south orientation.
The third (outer) enclosure
The third enclosure is 95 by 110 m; it is surrounded by a laterite wall breached by gopuras at the eastern and western ends. Neither pediment of the eastern gopura is in situ. The west-facing pediment is now located in the Musée Guimet in Paris. It depicts a scene from the Mahabhārata in which the Asura brothers Sunda and Upasunda fight over the Apsara Tilottama.
The east-facing pediment is lying on the ground. It depicts a scene from the Rāmāyaṇa in which a demon seizes Rama's wife Sita. Most of the area within the third enclosure is occupied by a moat divided into two parts by causeways to the east and west.

The second enclosure
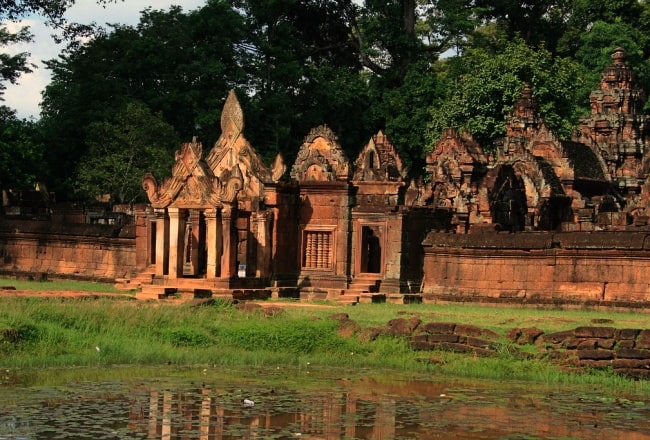
The second enclosure sits between an outer laterite wall measuring 38 by 42 m, with gopuras at the eastern and western ends, and a brick inner enclosure wall, measuring 24 by 24 m. The western gopura features an interesting bas relief depicting the duel of the monkey princes Vāli and Sugriva, as well as Rāma's intervention on Sugrīva's behalf.
The inner enclosure wall has collapsed, leaving a gopura at the eastern end and a brick shrine at the western. The eastern pediment of the gopura shows Śiva Nataraja; the west-facing pediment has an image of Karaikal Ammaiyar, one of the three women saints amongst the sixty three Nayanmars (hounds of Śiva).
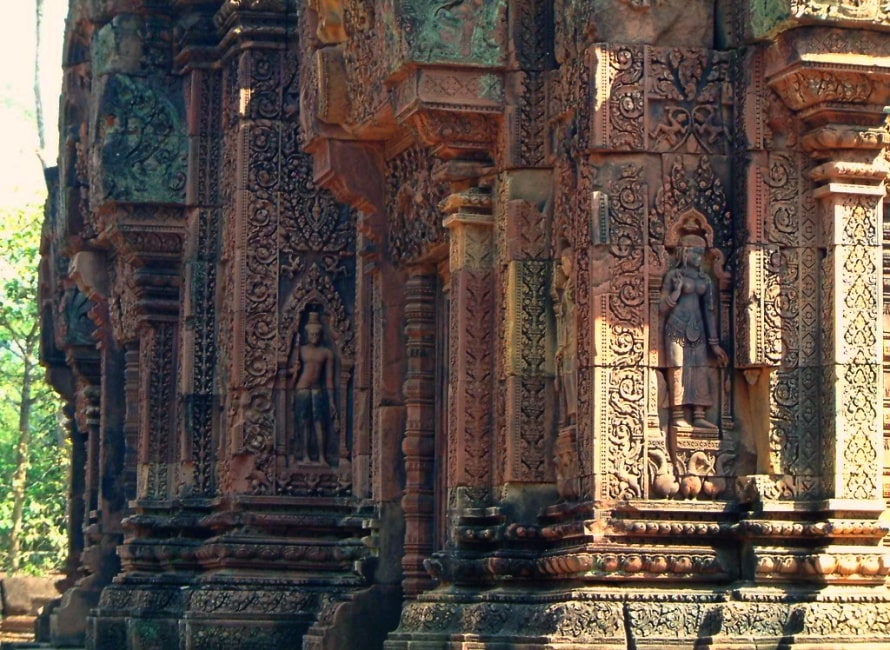
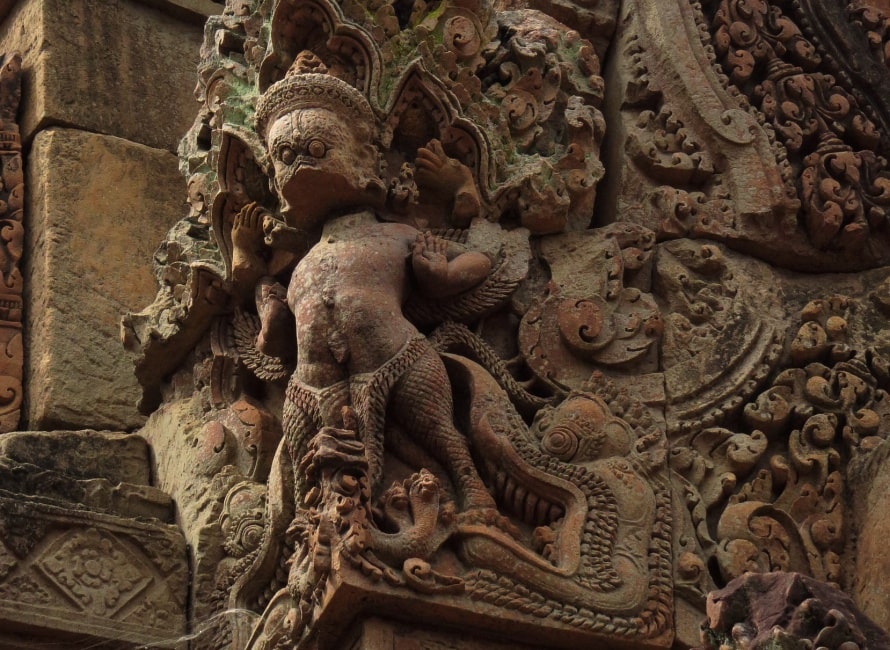
Likewise, the laterite galleries which once filled the second enclosure (one each to north and south, two each to east and west) have partially collapsed. A pediment on one of the galleries shows the lion-man Narasiṃha clawing the demon Hiranyakashipu.
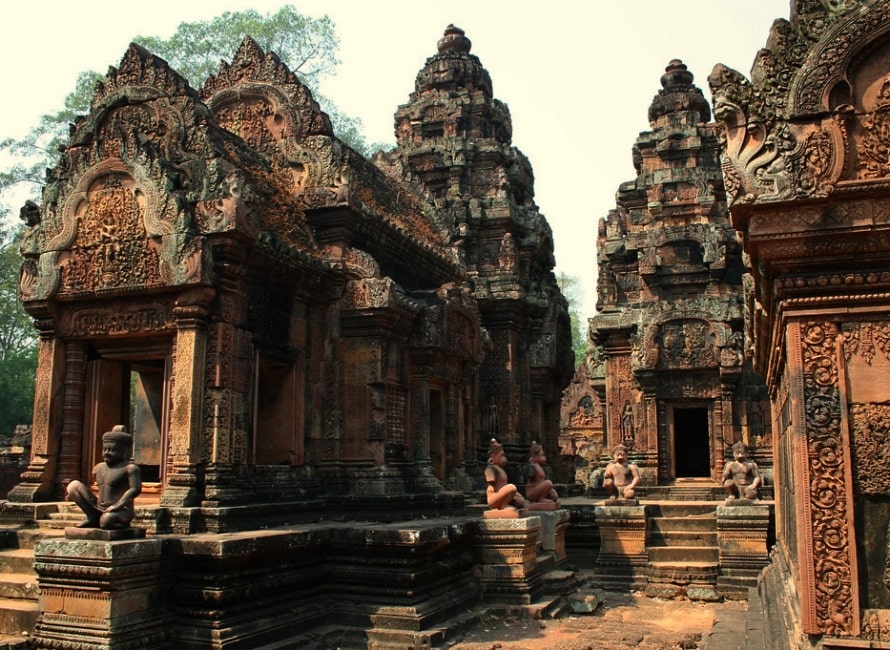
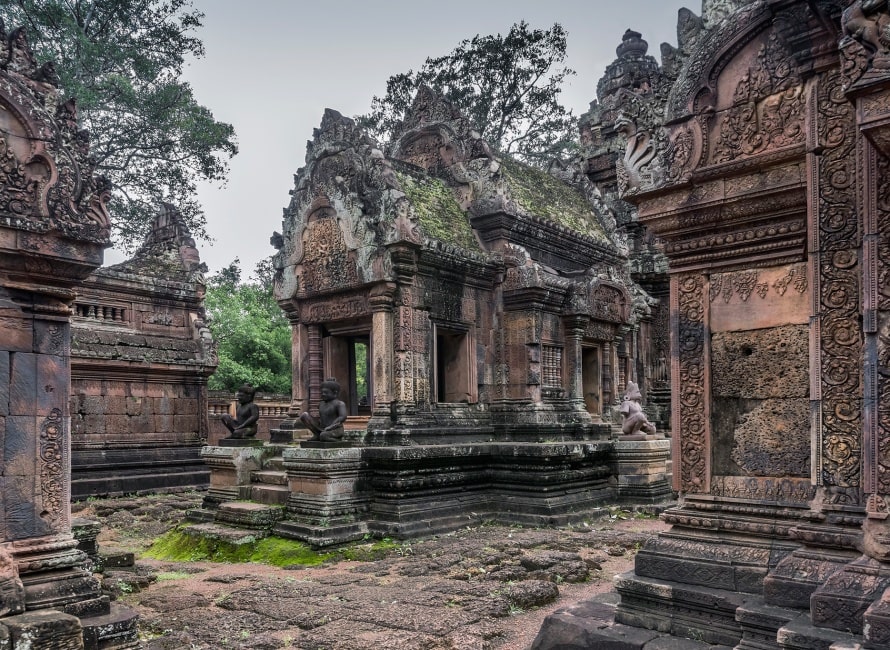
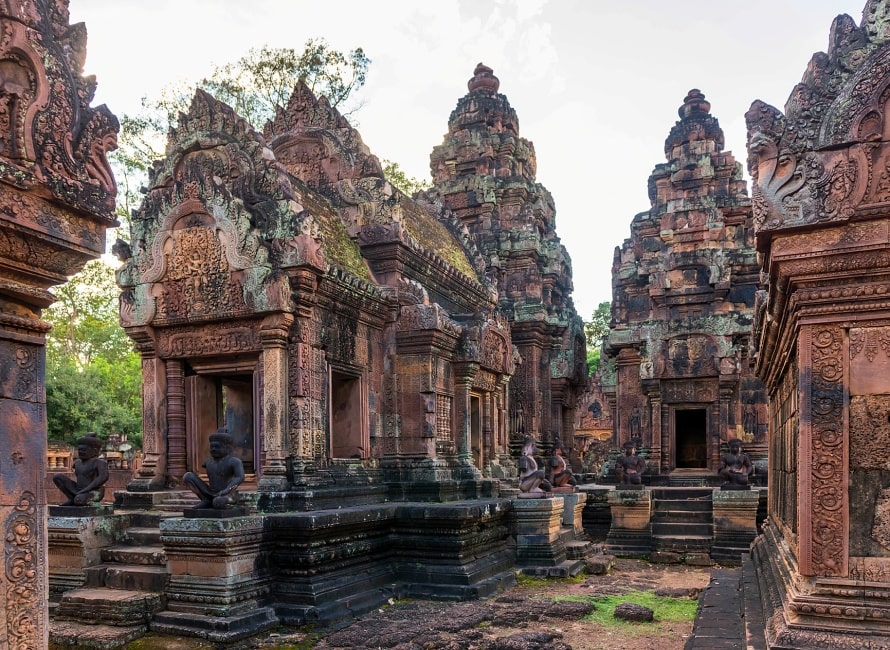
The first (inner) enclosure
Between the gopuras on the collapsed inner wall are the buildings of the inner enclosure: a library in the south-east corner and another in the north-east corner, and in the centre the sanctuary set on a T-shaped platform 0.9 m high. Besides being the most extravagantly decorated parts of the temple, these have also been the most successfully restored (helped by the durability of their sandstone and their small scale). In 2010, the first enclosure is open to visitors again, but the inner temples are roped off and inaccessible.

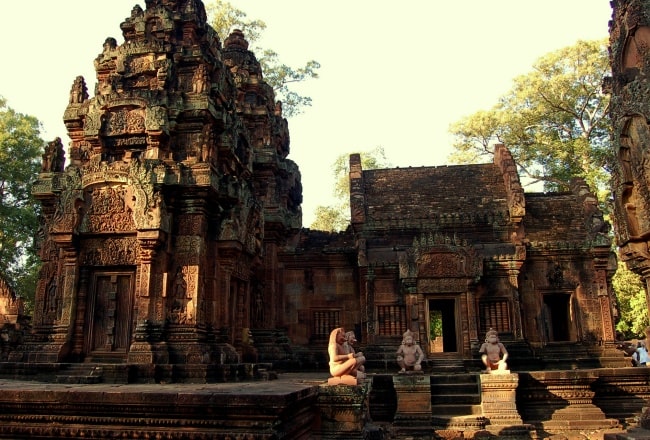
The libraries
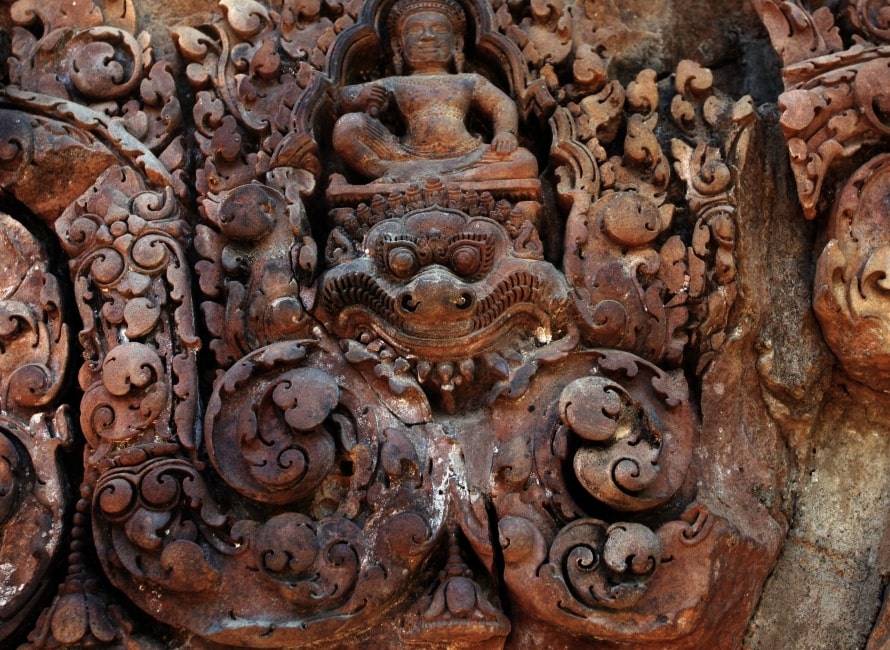
The two libraries are of brick, laterite and sandstone. Each library has two pediments, one on the eastern side and one on the western. According to Maurice Glaize, the four library pediments, "representing the first appearance of tympanums with scenes, are works of the highest order. Superior in composition to any which followed, they show true craftsmanship in their modelling in a skilful blend of stylisation and realism."
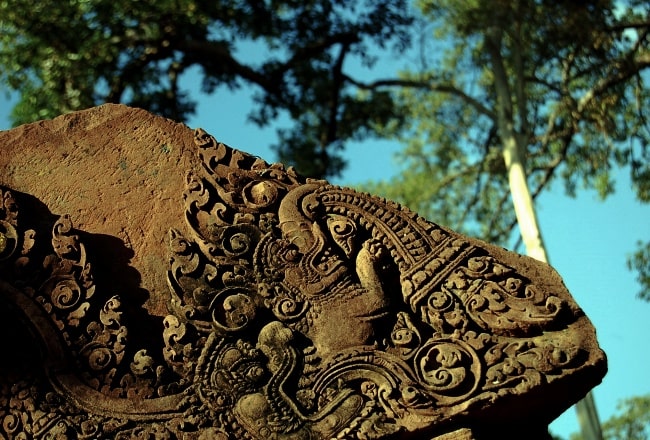
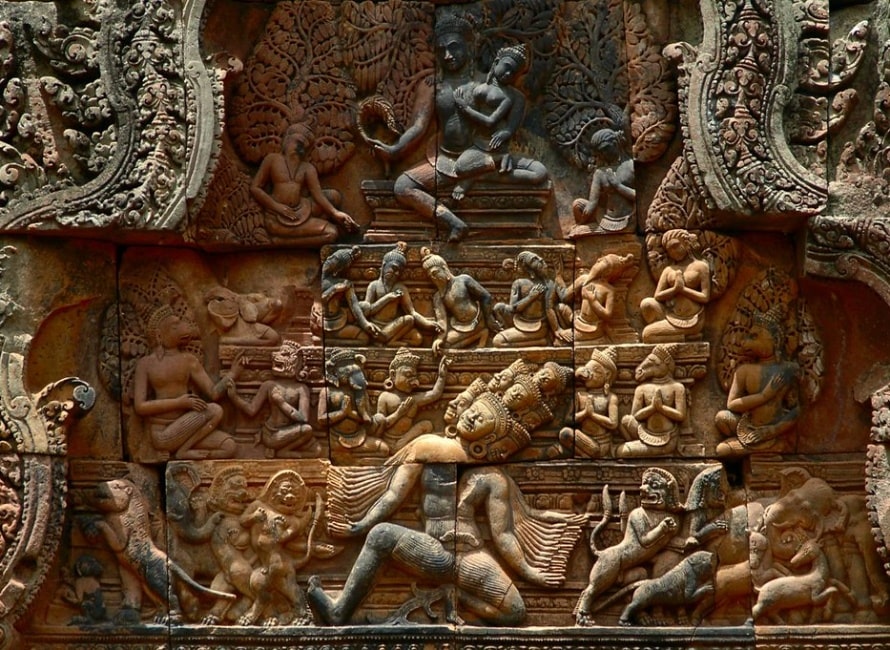
The east-facing pediment on the southern library shows Śiva seated on the summit of Mount Kailāsa, his mythological abode. His consort Umā sits on his lap and clings anxiously to his torso. Other beings are also present on the slopes of the mountain, arranged in a strict hierarchy of three tiers from top to bottom.
In the top tier sit bearded wise men and ascetics, in the middle tier mythological figures with the heads of animals and the bodies of humans, and in the bottom tier large animals, including a number of lions. In the middle of the scene stands the ten-headed demon king Rāvaṇa.
He is shaking the mountain in its very foundations as the animals flee from his presence and as the wise men and mythological beings discuss the situation or pray. According to the legend, Śiva stopped Rāvaṇa from shaking the mountain by using his toe to press down on the mountain and to trap Rāvana underneath for 1000 years.
The west-facing pediment on southern library shows Śiva again seated on the summit of Mount Kailāsa. He is looking to his left at the god of love Kāma, who is aiming an arrow at him. Umā sits to Śiva's right; he is handing her a chain of beads. The slopes of the mountain are crowded with other beings, again arranged in a strict hierarchy from top to bottom.

Just under Śiva sits a group of bearded wise men and ascetics, under whom the second tier is occupied by the mythological beings with the heads of animals and the bodies of humans; the lowest tier belongs the common people, who mingle sociably with tame deer and a large gentle bull.
According to the legend, Kāma fired an arrow at Śiva in order to cause Śiva to take an interest in Umā. Śiva, however, was greatly angered by this provocation, and punished Kāma by gazing upon him with his third eye, frying Kāma to cinders.
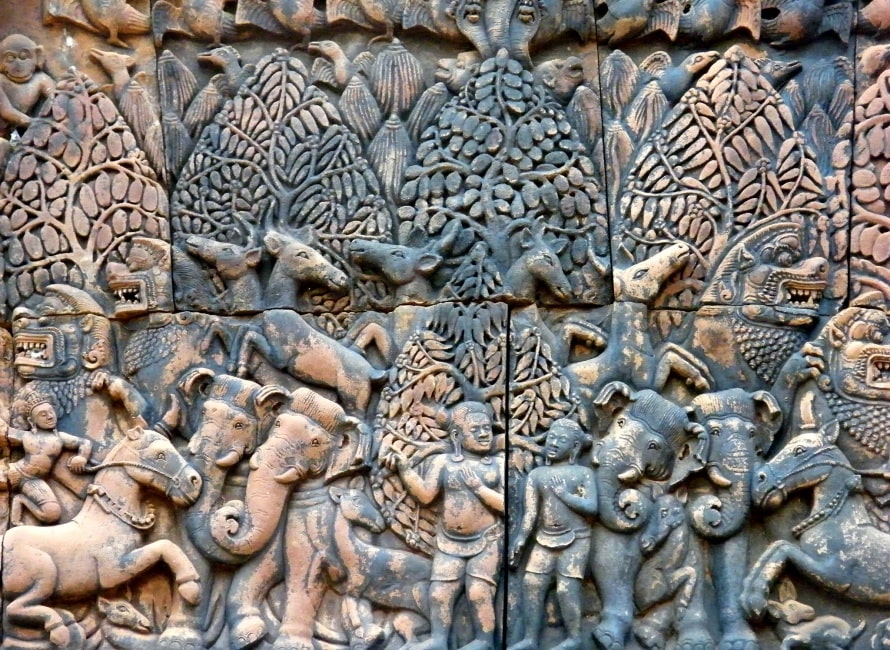
The east-facing pediment on the northern library shows the god of the sky Indra creating rain to put out a forest fire started by the god of fire Agni for purposes of killing the nāga king Takshaka who lived in Khandava Forest. The Mahābhāratan heroes Kṛṣṇa and Arjuna are shown helping Agni by firing a dense hail of arrows to block Indra's rain. Takṣaka's son Aśvasena is depicted attempting to escape from the conflagration, while other animals stampede about in panic.
The west-facing pediment on the northern library depicts Kṛṣṇa slaying his wicked uncle Kamsa.
The sanctuary
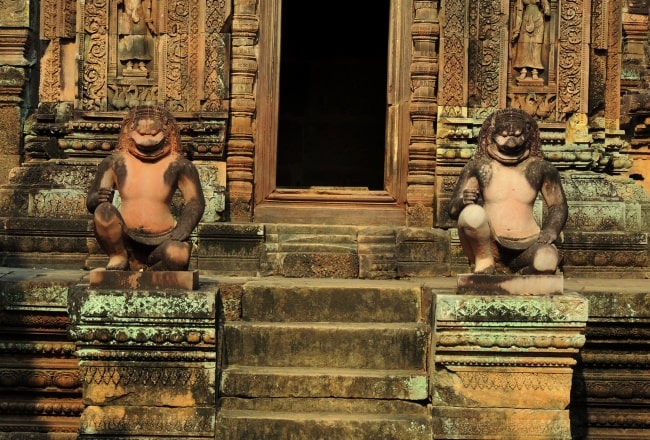
The sanctuary is entered from the east by a doorway only 1.08 m in height: inside is an entrance chamber (or maṇḍapa) with a corbelled brick roof, then a short corridor leading to three towers to the west: the central tower is the tallest, at 9.8 m. Glaize notes the impression of delicacy given the towers by the antefixes on each of their tiers. The six stairways leading up to the platform were each guarded by two kneeling statues of human figures with animal heads; most of those now in place are replicas, the originals having been stolen or removed to museums.

The burning of the Khandava forest carvings
One of the pediments on the library to the right of the entrance shows a magnificent depiction of the burning of the Khandava forest, a story from the Mahabharata, one of the great Indian epics. The story goes that the Pandava brothers wanted the Khandava forest cleared, after which Arjuna and Krishna decided to burn it down. The depiction shows Indra riding his three headed elephant protecting the forest by unleashing massive rainfall on the forest. Arjuna and Krishna however, create a shield of arrows hanging over the forest to stop the water.
Ravana lifting Mount Kailash carvings
Another carving shows a scene of an Indian legend, Ravana lifting Mount Kailash. Ravana, the King of Lanka depicted with ten heads and twenty arms lifts the Mount Kailash, on top of which lives the God Shiva. The story goes that when Ravana lifted the mountain, Shiva pushed it down with a single toe, trapping Ravana under it. After Ravana praised Shiva for a thousand years, he was finally set free. carvings show Ravana lifting the mountain and Shiva and Uma holding it down.






 04/03/2026
04/03/2026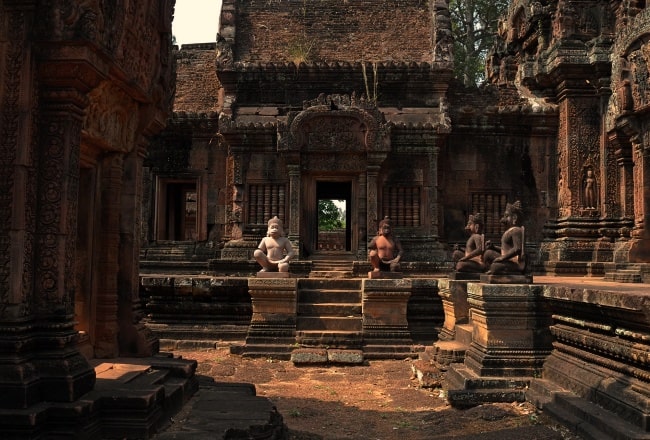








































Jolie LIEMMy name is Jolie, I am a Vietnamese girl growing up in the countryside of Hai Duong, northern Vietnam. Since a little girl, I was always dreaming of exploring the far-away lands, the unseen beauty spots of the world. My dream has been growing bigger and bigger day after day, and I do not miss a chance to make it real. After graduating from the univesity of language in Hanoi, I started the exploration with a travel agency and learning more about travel, especially responsible travel. I love experiencing the different cultures of the different lands and sharing my dream with the whole world. Hope that you love it too!